Diabetes Management in Seniors: Tips for Healthy Living and Home Care
Managing diabetes in seniors can be challenging, but with the right approach and support, it is possible to maintain a healthy lifestyle and reduce the risk of complications. As people age, their bodies undergo changes that can affect blood sugar levels, medication tolerance, and the ability to follow strict routines. That’s why having a tailored plan for diabetes management is crucial for seniors. Below, we provide essential tips for healthy living and home care that can help seniors manage their diabetes effectively.
1. Understand the Basics of Diabetes
Diabetes is a condition that affects how the body uses blood glucose (sugar). In seniors, the two main types are:
- Type 1 Diabetes: The body does not produce insulin, requiring lifelong insulin therapy.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The body does not use insulin properly, and this form of diabetes is more common in seniors.
Proper management includes maintaining stable blood sugar levels, eating a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and taking prescribed medications.
2. Create a Balanced Meal Plan
A balanced diet plays a vital role in managing diabetes. Seniors should consume a variety of nutrient-dense foods while keeping an eye on carbohydrates, which directly affect blood sugar levels.
Meal Tips:
- Portion Control: Control the portion sizes, especially for foods high in carbs, like bread, pasta, and starchy vegetables.
- Regular Meals: Eat meals at consistent times throughout the day to help stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Choose Whole Grains: Opt for whole grains like oats, brown rice, and quinoa over refined grains to promote better glucose management.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Aim to consume a variety of fruits and non-starchy vegetables. These provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
- Healthy Fats and Proteins: Include lean proteins (like chicken, fish, beans, and legumes) and healthy fats (like olive oil, nuts, and avocados).
3. Stay Physically Active
Regular physical activity is essential for managing diabetes and improving overall health. For seniors, even moderate exercise can have significant benefits, such as improving insulin sensitivity, enhancing circulation, reducing stress, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Activity Suggestions:
- Walking: A gentle and low-impact way to stay active. Aim for 30 minutes of walking, five days a week.
- Chair Exercises: For those with limited mobility, chair exercises like seated leg raises, arm stretches, or resistance band exercises can help maintain strength and flexibility.
- Swimming or Water Aerobics: These are great options for seniors with joint issues or arthritis, as they provide a low-impact workout.
Before starting any exercise routine, it’s best for seniors to consult their healthcare provider.
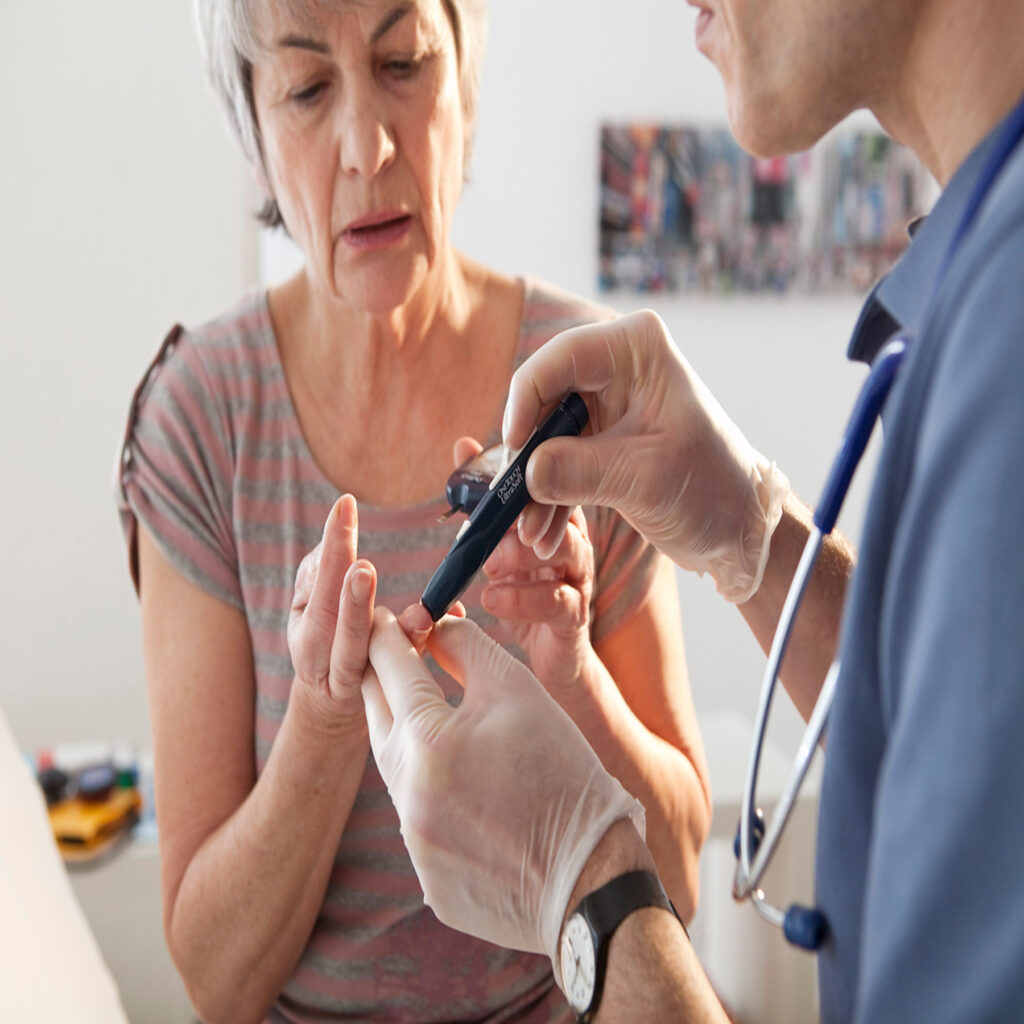
4. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels Regularly
Regular blood glucose monitoring is vital to help seniors understand how different foods, activities, and medications affect their blood sugar levels. The frequency of testing can vary based on the type of diabetes, medication, and doctor recommendations.
Tips for Effective Monitoring:
- Keep a Log: Track daily blood sugar readings, meals, activities, and any symptoms. This can help identify patterns and make it easier for healthcare providers to adjust treatment as needed.
- Know the Target Ranges: Understand your individual target blood sugar ranges, which can differ based on age, type of diabetes, and overall health.
5. Medication Management
Many seniors with diabetes require medication to manage their condition, which may include oral medications, insulin, or other injectable medications. It’s important to take these as prescribed.
Medication Management Tips:
- Set Alarms or Reminders: Use smartphone alarms, pill organizers, or medication reminders to ensure that medications are taken at the correct times.
- Watch for Side Effects: Be aware of potential side effects, such as low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), which can lead to symptoms like dizziness, confusion, or shakiness. Always have quick-acting sugar sources like glucose tablets or fruit juice available in case of low blood sugar episodes.
- Regular Checkups: Regularly visit healthcare providers to review medications and make any necessary adjustments.
6. Maintain Hydration
Staying hydrated is essential for seniors, as dehydration can affect blood sugar levels. Encourage regular fluid intake throughout the day, focusing on water, herbal teas, or low-sugar drinks.
7. Promote Foot Care
Diabetes can lead to reduced circulation and nerve damage, increasing the risk of foot issues like sores, blisters, or infections. For seniors, maintaining proper foot care is critical.
Foot Care Tips:
- Daily Checks: Examine feet daily for cuts, blisters, redness, or swelling.
- Wear Proper Footwear: Use comfortable, well-fitting shoes that provide support and reduce the risk of injury.
- Moisturize Regularly: Keep feet moisturized, but avoid applying lotion between toes, as excess moisture can lead to fungal infections.
8. Get Regular Health Screenings
Routine health screenings are essential for seniors with diabetes to prevent and manage complications. This includes regular eye exams to detect early signs of diabetic retinopathy, dental checkups for oral health, and kidney function tests.
Ask Your Healthcare Provider About:
- A1C Levels: Regular A1C tests to monitor average blood glucose over the past 2-3 months.
- Cholesterol & Blood Pressure Checks: Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease, so keeping track of cholesterol and blood pressure is crucial.
- Flu & Pneumonia Vaccinations: Seniors with diabetes are more susceptible to infections, so staying up-to-date with vaccinations is important.
9. Seek Support from Family and Caregivers
Family members and caregivers play an important role in the day-to-day management of diabetes in seniors. They can assist with medication reminders, meal preparation, transportation to doctor’s appointments, and offering emotional support. Open communication between seniors, their caregivers, and healthcare professionals can enhance diabetes management and improve overall well-being.
Conclusion
Living with diabetes as a senior doesn’t mean life has to be limited or overly restricted. With proper home care, healthy habits, and the right support system, managing diabetes effectively is possible. By focusing on balanced nutrition, regular exercise, blood sugar monitoring, and routine health checks, seniors can lead a healthy and active lifestyle while keeping their diabetes in check.